Troubleshooting
This sections provide solutions to some common problems. You are welcome to contribute more Q&A's to the section.
SSH Local Forwarding
The SSH forwarding command is successful if it directly returns without any output.
$ ssh -fN -L 3389:localhost:3389 ubuntu@roselab1.ucsd.edu -p port -i /path/to/keyfile
$ # No outputIf it hangs, it means that you cannot log in to your SSH shell. Double-check that you have entered the correct hostname, port, and key path.
$ ssh -fN -L 3389:localhost:3389 ubuntu@roselab1.ucsd.edu -p wrong-port -i /path/to/keyfile
# HangingIf it returns with the following message, there is already a service running on the local port. You can identify the service by using lsof.
$ ssh -fN -L 3389:localhost:3389 ubuntu@roselab1.ucsd.edu -p port -i /path/to/keyfile
bind [127.0.0.1]:3389: Address already in use
channel_setup_fwd_listener_tcpip: cannot listen to port: 3389
Could not request local forwarding.
$ lsof -i :3389
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE
OtherApp 815 user 20u IPv4 0xb8238ac165eb1fd3
$ kill -9 815 # Kill the processIf you don't want to kill the process, you can forward another local port to the remote port.
$ ssh -fN -L 3389:localhost:3340 ubuntu@roselab1.ucsd.edu -p port -i /path/to/keyfile
$ # You can then connect to RDP at rdp://localhost:3340Docker in Container
You may see the following error when trying to pull a Docker image in your container:
Pulling netflow ... extracting (100.0%)
ERROR: failed to register layer: Error ...This is because Docker's overlay2 storage driver does not work well with LXC containers due to kernel limitations.
Solution
To run Docker with current versions inside LXC containers, use the fuse-overlayfs storage driver. See our comprehensive Docker in LXC guide for detailed setup instructions.
Machine Learning Threshold
We recommend the our users to regularly inspect their resource usage during GPU tasks to optimize their tasks.
CPU Threshold
When you are assigned more cores than you need, you may see the following patterns:
- High CPU usage
- The system (kernel) is busier than the user
- Low GPU utility, which fluctuates over time
This is because of a well-known problem of PyTorch: it tries to use as many CPU cores as possible. All cores have almost nothing to do, but the overhead of communication (in kernel mode) becomes very high. GPU utility is heavily reduced because it needs to wait for the CPU.
Solution
You may manually limit the number of cores to use by using torch.set_num_threads. If you don't want to modify your scripts every time, you can contact the admin to limit the number of cores available to you. The image below shows the improved performance after limiting the number of cores from 56 to 12.
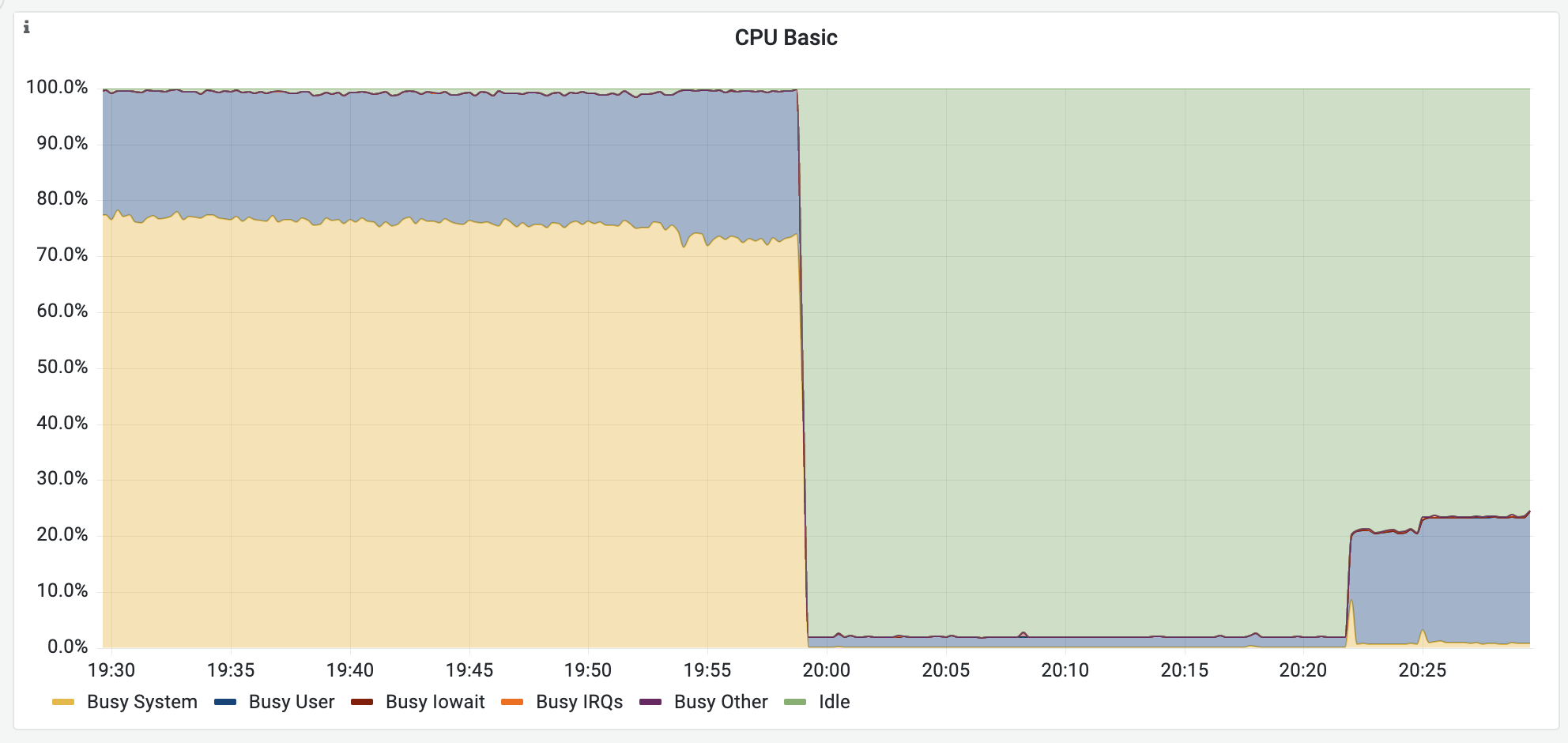
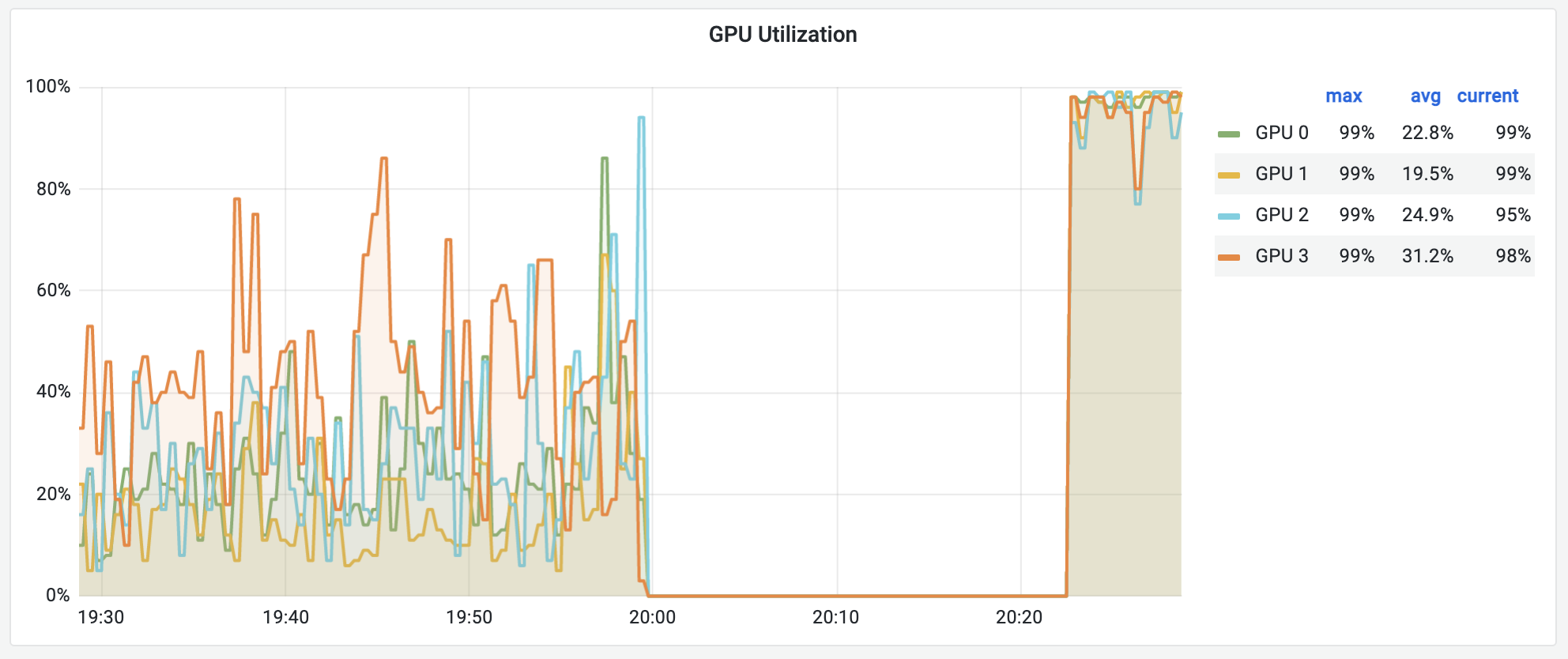
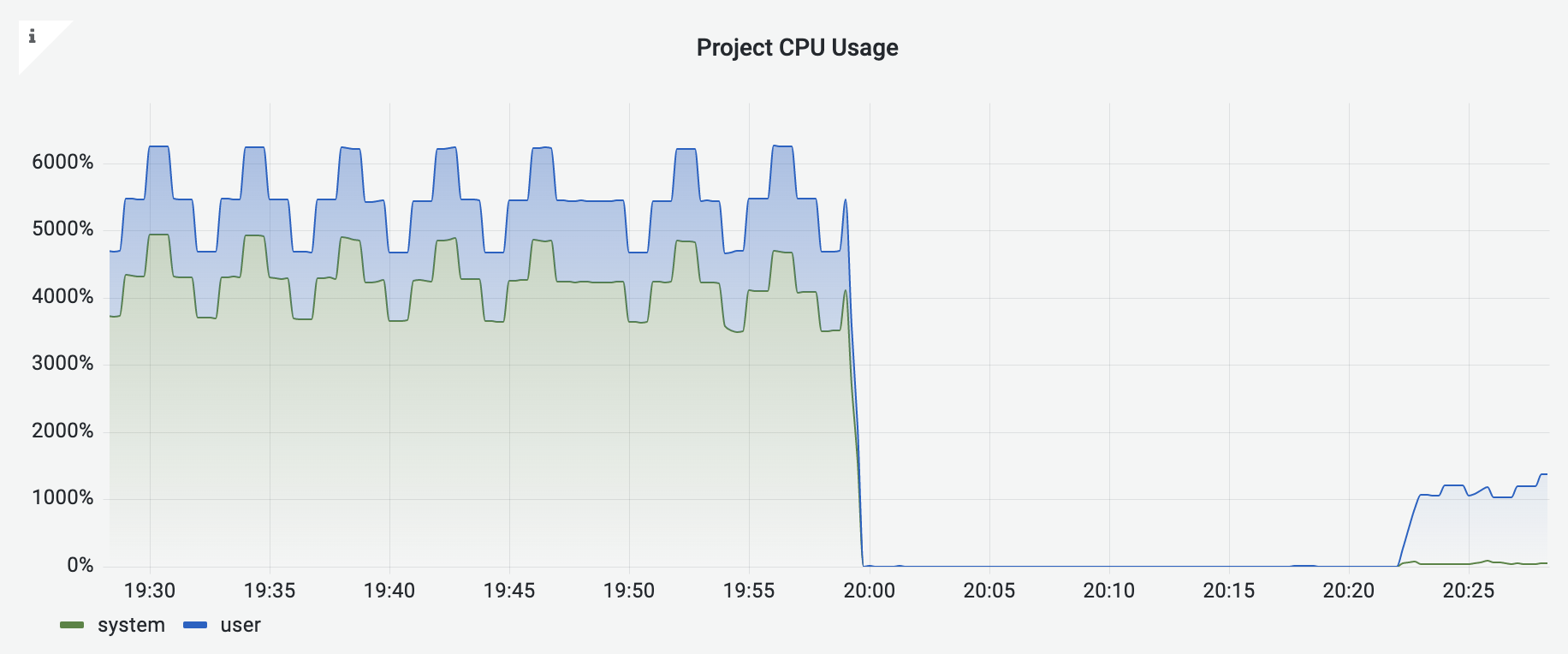
Disk Threshold
When running machine learning tasks, large datasets are often loaded from disk. But you should generally expect your disk I/O usage to be relatively low, because most data is prefetched into memory. If you notice that both CPU and GPU utilizations are low, it likely means that both CPU and GPU are waiting for data to be loaded from disk.
Solution
PyTorch has a build-in data prefetching mechanism. While the GPU is training a batch, torch.utils.data.DataLoader will load the data for next batch. By default, there is a total of 2 * num_workers batches prefetched across all workers. The num_workers is by default 0. If you face slow disk reading speed, consider increasing the number of workers.
NVIDIA Driver Issues
Driver/Library Version Mismatch
If you see the error message:
Failed to initialize NVML: Driver/library version mismatchThis indicates that your container's NVIDIA driver is out of sync with the host system.
Cause
The host and container NVIDIA driver versions must match exactly. This mismatch typically occurs after:
- Server maintenance or reboots
- Host driver updates
- Container restoration from backup
WARNING
You cannot change host driver versions yourself - these are managed by the admin and documented in the config table.
Solution
Use the NVIDIA upgrade script (recommended):
bashsudo /utilities/nvidia-upgrade.sh sudo rebootWait for automatic reboot: After running the script, your container will reboot to apply the new driver.
Verify the fix: After reboot, check that CUDA is working:
bashnvidia-smi python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"
Important
Never install nvidia-driver through your package manager (apt, yum, etc.). This will break GPU passthrough and prevent your container from accessing GPUs. Always use the provided upgrade script.
GPU Not Available (NVSwitch Servers Only)
If your GPUs are completely undetectable — nvidia-smi shows no devices, and torch.cuda.is_available() returns False — but other users on the same server are unaffected, this is a startup ordering issue specific to NVSwitch-based GPU servers (currently roselab5 with H200 GPUs).
$ nvidia-smi
No devices were found
# or
$ python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"
FalseINFO
This issue does not affect roselab2/3 (RTX 4090) or roselab4 (L40S), because those GPUs use PCIe direct passthrough and do not require NVIDIA Fabric Manager.
Cause
NVSwitch-based GPUs (H200, H100, A100 SXM, etc.) require the NVIDIA Fabric Manager service to be fully initialized before CUDA can detect the GPUs. After a host reboot, if your LXC container starts before the Fabric Manager finishes initializing, the GPU device nodes (/dev/nvidia*, /dev/nvidia-nvlink, /dev/nvidia-nvswitch*) are not properly injected into the container.
This is a startup race condition — containers that happen to start earlier hit the uninitialized window, while containers that start later (after Fabric Manager is ready) work fine. This explains why the issue affects some users but not others on the same server.
Solution
The upgrade script re-establishes the user-space driver files and device node mappings inside the container, and the reboot remounts everything:
sudo /utilities/nvidia-upgrade.sh
sudo rebootAfter reboot, verify:
nvidia-smi
python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"TIP
If GPUs are missing across all your containers on the same server, each container needs the fix independently — run the script and reboot on each affected container.
Current Driver Version
As of the latest server migration (October 2025), all NVIDIA drivers have been upgraded to version 580.95.05. You can verify your driver version with:
nvidia-smi | grep "Driver Version"File Permissions on /data
Cannot Use chown/chgrp on /data
If you find that you cannot change file ownership or group on /data using chown or chgrp commands, even with sudo, this is expected behavior due to NFS security features.
$ sudo chown username:groupname /data/some-folder
# Operation not permitted or no effectCause
The /data directory is a network-mounted filesystem (NFS) that is physically hosted on roselab1 and mounted on all other servers (roselab2-5). NFS has security restrictions that prevent non-root users from changing file ownership, and LXC container root users are not considered "true" root users from the NFS perspective.
This is not a bug but a security feature of network-mounted filesystems to prevent unauthorized ownership changes across the network.
Solution
To change file permissions or ownership on /data:
SSH into your container on roselab1 (where
/datais physically hosted):bashssh ubuntu@roselab1.ucsd.edu -p your-portRun chown/chgrp commands there:
bashsudo chown username:groupname /data/your-folder sudo chmod 755 /data/your-folderThe changes will be immediately visible across all servers since
/datais synchronized.
TIP
If you need to perform bulk permission changes, it's most efficient to do them from roselab1 where the storage is physically located.
